Inspection and Condition Control
Inspection, measurement and diagnostic techniques allow us to access the condition of each piece of equipment and to define the operations to be carried out, which must consider the scheduled maintenance planned tasks. The inspection and condition control services assess the condition of the equipment in its operating context, diagnose abnormal situations and develop approaches to analyzing breakdowns.
Our clients
Advantages

Early Fault Detection
Detection of the failure mechanisms in development and its monitoring.
Fault Detection Accuracy
Identification and characterisation of the equipment at fault and its failure mode(s).

Unplanned Downtime Reduction
Prior preparation of materials, services, M.O. before the scheduled intervention.
O&M Cost Reduction
Cost reduction to avoid unplanned corrective interventions.

Increased efficiency
Reduced downtime by improving planned corrective interventions and/or anticipating preventive ones.

Scalability
Increased intervention capacity by anticipating team loads.
Measurement Techniques
Vibration Analysis
Characterisation of equipment condition through mechanical vibration analysis in the time and frequency domains. Detection of degraded components or anomalous behaviour, e.g. misalignment, imbalance, resonance, etc.

Thermography
Characterization of equipment health by analyzing infrared emissions to detect overheating, loosening or loss of insulation.

Gas Leak Detection
Characterization of compressed air or other gas leaks using ultrasound technology, avoiding energy losses, development failures and waste costs.

Thickness measurement
Determination of pipes, tanks or structural components or paint layers thickness using ultrasound techniques.
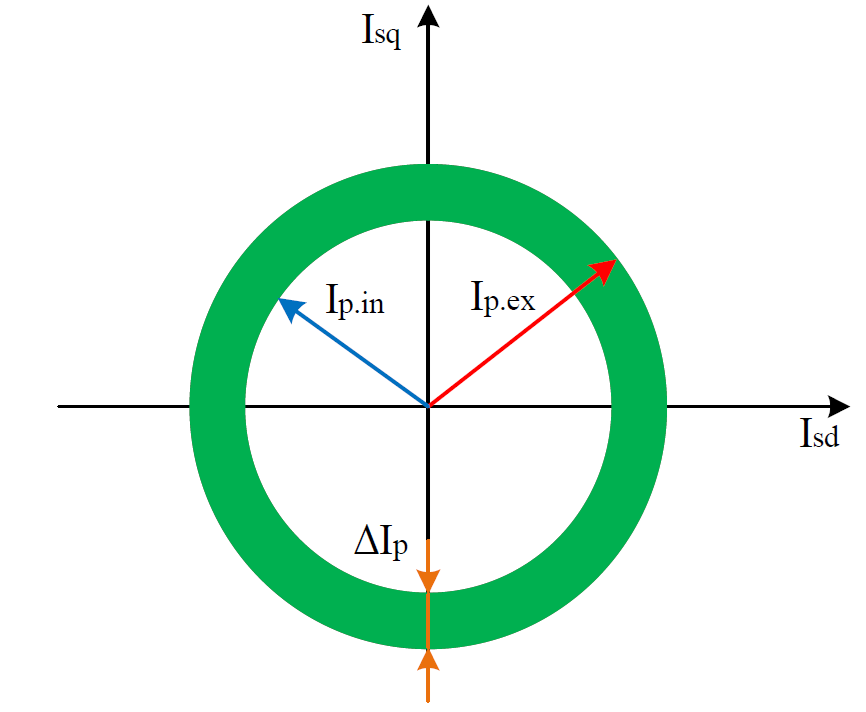
Condition of electrical machines
Characterization of the operational state of electrical machines through Park vector analysis. It detects degraded components or anomalous behaviour such as phase imbalance, broken bars, poor insulation, etc.

Non-destructive testing
Characterization of the condition of components through the application of penetrating liquids, or magnetic particle techniques, x-rays or ultrasound, which makes it possible to detect degradation or deficiencies.
Interventions

Status and diagnostic monitoring
Monitoring the condition of equipment, diagnosing possible developing faults and predicting their evolution by monitoring parameters collected continuously or periodically.

One-time off and Periodic Interventions
Carrying out specific balancing operations on site – on 1 or more planes. Alignments – on shaft lines – collinear systems or with gimbals. Inspections on receipt of work.

Definition of inspection plans
Definition of inspection plans to frame condition control techniques, according to the architecture and technical characterisation and operational context of each piece of equipment, linked to maintenance plans.
Dynamic modelling
Creation of models to determine the dynamic behaviour of structures and equipment, both in free and forced regimes. Predicting vibration modes and resonances. Analysing dynamic behaviour and proposing changes to the dynamic characteristics of systems or the way they are operated in order to alter this.

Fault diagnosis
Failure analysis, in the context of the use of equipment and structures, investigating the root cause. Definition of weak points and proposals for overcoming them.





















